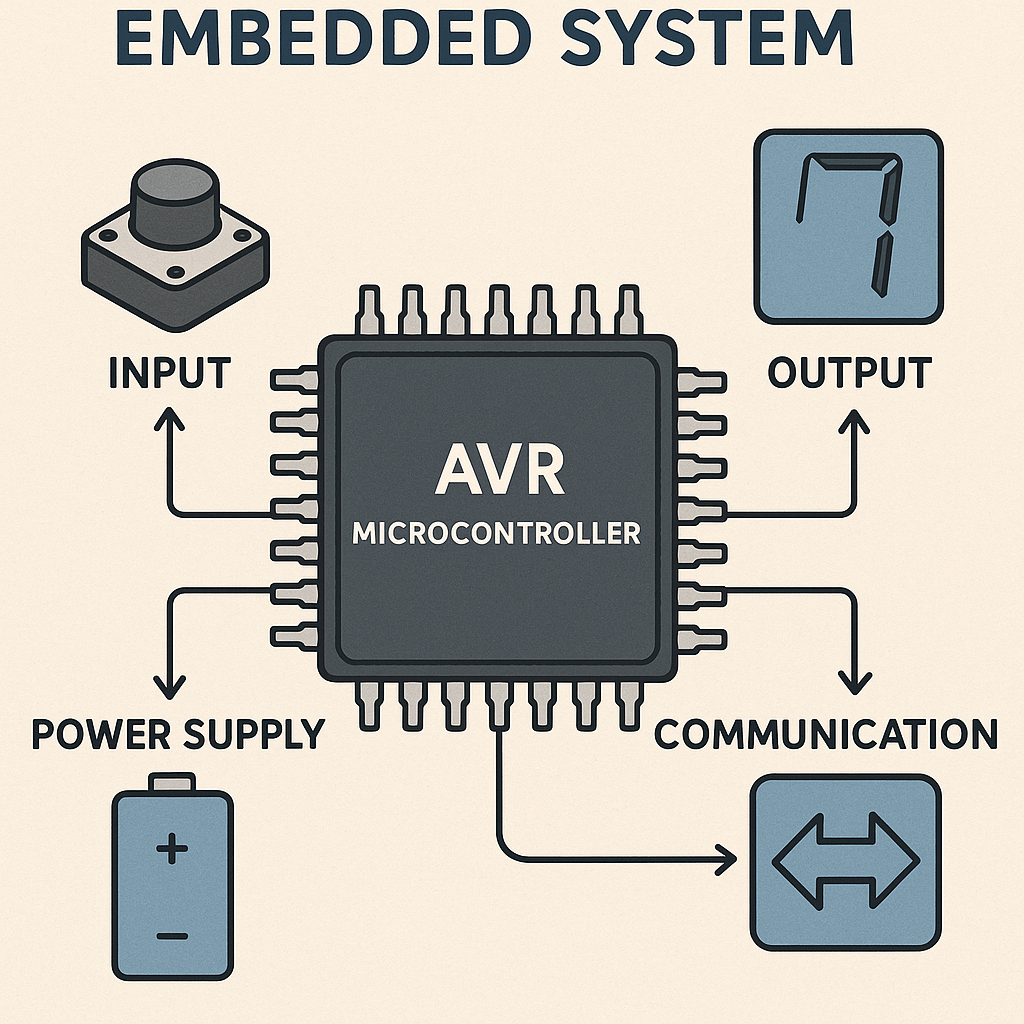
Embedded System with AVR Microcontroller
Course Objective:
To understand the fundamental concepts of embedded systems and microcontrollers.
To explore the architecture and features of the AVR microcontroller family.
To understand the memory organization of AVR microcontroller.
To gain proficiency in programming AVR microcontrollers using the C language.
To understand and implement peripheral interfacing with real-world applications.
To develop embedded solutions using timers, interrupts, serial communication, and
protocols like SPI and I2C.
Course Objective:
To understand the fundamental concepts of embedded systems and microcontrollers.
To explore the architecture and features of the AVR microcontroller family.
To understand the memory organization of AVR microcontroller.
To gain proficiency in programming AVR microcontrollers using the C language.
To understand and implement peripheral interfacing with real-world applications.
To develop embedded solutions using timers, interrupts, serial communication, and
protocols like SPI and I2C.
Introduction to Embedded Systems: Embedded systems: introduction, characteristics, elements and applications. Design metrics: NRE cost, unit cost, time to market, safety, maintenance, size, cost and power dissipation. Software development tools: editor, assembler, linker, compiler, IDE, ICE, programmer and simulator. Microcontroller & Architectures: History, introduction, classification, applications. Differences between microcontroller and microprocessor, criteria for choosing a microcontroller. Architectures - Harvard and Von-Neumann architecture, RISC vs CISC. Concept of pipelining. AVR Architecture: Overview of AVR, classification of AVR family, AVR (ATmega16/32) architecture, AVR processor memory map, CPU registers, ALU, I/O ports, peripherals in AVR. Programming of AVR in C: basic structure, data types, operators, library files, delay functions and bitwise operation syntax. Simple C programs: Data transfer operation, arithmetic operation, decision making and code conversion. AVR Timer Programming: introduction, difference between timer and counter operation, Basic SFR Registers used – Timer 0, 1 & 2, C programs for delay generation, counter Programming. AVR Serial Port Programming: Basics of serial communication (serial vs parallel, simplex vs duplex), difference between Asynchronous & synchronous communication, USART operation, SFR used, C programs for data transmission and reception. I2C and SPI: introduction, specifications, bus signals, master-slave configuration, error handling and addressing. SFR used in AVR, C programs to transfer and receive information. On-chip ADC: features, block diagram, operation, SFR used, C programs to convert the analog signal to digital. I/O device interfacing: LED, push button, buzzer, seven segment display, Thumbwheel switch, DC and stepper motor, relay interfacing, 16*2 LCD interfacing, DAC interfacing (waveform generation using DAC). Case studies: Traffic Light controller using AVR, Single digit event counter using opto-interrupter and SSD, Real time clock using IC DS1307 chip, temperature monitoring system using LM35 sensor, smart phone controlled devices using Bluetooth module HC05.
- INTRODUCTION TO ATMEL Unlimited
- INTRODUCTION TO ATMEL Unlimited